ORIGINS - Maps and Short History
HOME PAGE
PEOPLE & HISTORY
| Origins
| Early History in SA
| Ancestors
LINEAGE IN SOUTHERN AFRICA
| Descendants
| Migration
| Botha/Blake
BOTHA POTPOURRI
| Coat of Arms
| Noteworthy Bothas
| Botha Appellations
GENERAL INFORMATION
| Information
| Research Ideas
| Own Research
The surname of BOTHA in South Africa is derived from two progenitors ("stamvaders").
The first progenitor, Friedrich Both (a1) came from Germany,
whilst the second, Samuel Friedrich Bode (a2), although he came
from Germany, is believed to have migrated there from France.
The Thirty Years' War (1618- 1648) left many of the German states in
a poor economic condition. Consequently many Germans, including
ex-soldiers, were drawn to the west by the wealth of the
Netherlands. Political boundaries did not imply a complete division
between the people living in the border regions, and from a
linguistic point of view there was not much of a difference
between German and Dutch. This was particularly true of the regional
dialects of the eastern Netherlands and western German regional
dialects with a strong Saxon influence.
a1 FRIEDRICH BOTH
Friedrich Both was born on 4th March 1653 in Wangenheim, about 8 kilometers
(5 miles) north west of Gotha (50.57° Latitude, 10.41° Longitude), in the
Province of Thuringia in the duchy of Saxe-Coburg-Gotha (see
History below).
MAPS
A map of Germany follows with Thuringia highlighted:

German map from German WWW Servers
The size of the state of Thuringia (Thüringen) is about 16 251 square
kilometers (6 000 square miles) and the population is estimated at
2 684 000 people in 1990. The capital is Erfurt.
A map of Thuringia follows with Gotha highlighted:
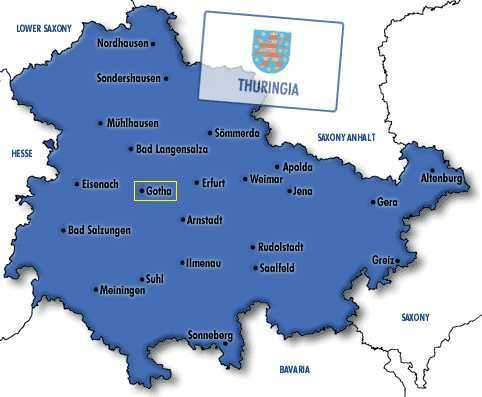
German map from German WWW Servers
The town of Gotha has about 50 000 inhabitants and distances from
other nearby towns are:
| Town |
Population |
Distance |
| Erfurt |
205 400 |
24 km |
| Bad Langensalza |
20 400 |
17 km |
| Eisenach |
44 700 |
26 km |
| Arnstadt |
26 000 |
23 km |
PHOTOS
The size of the town centre of Gotha can be seen from the following photograph:

Photo from Gotha - the Heart
The history of Thuringia can be traced back to 350 AD and the subsequent
events can be roughly divided into four separate periods.
First period - Until approximately 500 AD - The establishment of historical
Thuringia
The area's first occupants, the ancient Germanic tribe of Thuringians, were
conquered by Attila the Hun in the second quarter of the fourth century
and by 500 AD had freed themselves to establish their own kingdom. In 531
their king Irminfrid was defeated by the Franks and their kingdom placed
under their rule.
Second period - From 500 AD until 1485 - The era of central rule
To assert the Frankish king's authority, the area was ruled under authority
from the king by a succession of dukes and counts. The conversion of
Thuringia to Christianity was completed by the 8th century. The direct
line of German kings of the Saxon dynasty died out in 1024. They were
replaced by Louis the Bearded, a member of the Ludowing family. The
Ludowings ruled from 1039 until 1256. After a war lasting from 1256
to 1263, Henry the Illustrious obtained the territory. It was now
dominated by the Wettin dynasty of Saxony, who had emerged as princes
of the Holy Roman Empire.
Third period - From 1485 AD until 1918 - The era of duchies
The division of the Wettin lands in 1485 gave the major share to their
Ernestine line of family, who split Thuringia into several duchies, e.g.
Saxe-Coburg, Saxe-Weimar-Gotha, Saxe-Jena. The Ernestine family
continually distributed their lands between themselves and realigned
them from time to time. From 1826 there were four main duchies:
(1) the Grand Duchy of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach; (2) the Duchy of Saxe-Altenburg;
(3) the Duchy of Saxe-Meiningen-Hildburghausen; and (4) the Duchy of
Saxe-Coburg-Gotha. A map of this period obtained from Rootsweb or
can be seen by "clicking" on Map.
Fourth period - Post 1918 - Independent or Free State
After the German Revolution in 1918, the landgraves abdicated their
territories and these became Free States. In 1920 these territories
(except Coburg which joined Bavaria) merged to form a new Thuringia.
From 1946 to 1990 this area formed part of East Germany under Soviet
control.
FLAG OF THURINGIA
The Thuringian coat of arms has a rising lion, surrounded by eight stars.
The stars symbolize those areas that were united to reform Thuringia in
1920.

Graphic from
Flags of the World
a2 SAMUEL FRIEDRICH BODE
Samuel Friedrich Bode was born in 1730 in Lüneburg (53.15° Latitude, 10.23° Longitude),
Germany (see History below). In 1766
the family stayed in Hannover and Samuel left to go to Amsterdam to
join the VOC.
According to legend the family is believed to have migrated from
France (as Hugenots) possibly to the Netherlands and then to Germany.
The surname changed from Boudier (France) to Boodjee (Netherlands) to
Bode (Germany) and finally to Botha (South Africa).
MAPS
A map of Germany follows with Lower Saxony highlighted:

German map from
German WWW Servers
The size of the state of Lower Saxony (Nieder Sachsen) is about 47 338 square
kilometers (18 296 square miles) and the population is estimated at
7 190 000 people in 1988. The capital is Hanover.
A map of Lower Saxony follows with Lüneburg highlighted:

German map from German WWW Servers
The town of Lüneburg has about 65 800 inhabitants and distances from
other nearby towns are:
| Town |
Population |
Distance |
| Winsen |
30 900 |
19 km |
| Seevetal |
37 900 |
31 km |
| Uelzen |
35 300 |
34 km |
PHOTOS
The following photograph shows the brick houses next to the Ilmenau
river in Lüneburg which were built during the rich salt era:

Photo from Lüneburg Heath
Of special interest is the Salt Works of Lüneburg. Salt, the "White
Gold" of the Middle Ages, was produced by boiling the abundant
resources of pure salt water and using wood from the forest
surrounding the city. The Salt Works continued with the production of
salt for 1 024 years and was only closed in 1980.
The history of Lower Saxony is similar to the history of Thuringia
(see History above) as they were both ruled
by dukes, as a result of the Holy Roman Empire. The current day Lower
Saxony was established with the merger of Hanover, Brunswick,
Oldenburg and Schaumburg-Lippe.
Brunswick - Pre 1919
The area was ruled by the Welf dukes as the duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg
until 1635 when it was divided among the children of duke Frederick
Ulrich and became the duchy of Brunswick until 1918. In 1919 it
became a Free State.
Hanover - Pre 1946
The electorate of Hanover grew out of one of the divisions of the
possessions of the house of Brunswick-Lüneburg. In 1636 Duke Georg
established his residence in the city of Hanover after he had
inherited certain principalities. His principalities soon came to be
named after its principal city. The growth of Hanover was solely
attributed to the skill of its rulers. Through the marriage of one of
the sons to Sophia Dorothea, George I of England's only daughter, a
link to the British Royalty had been made. Although Sophia became
electress, she never succeeded to the throne; she died a few weeks
before. Her son, the elector George Louis, ascended the British throne
as George I. The 123 year association between the British throne and
Hanover had started. The British kings then ruled Hanover from a
distance through a privy council.
In 1814, after the defeat of Napoleon, the area was enlarged and was
also elevated to a kingdom. In 1837 the union with Britain was broken
as the law of succession in Hanover did not allow female succession
if a male heir was still living. Hanover did not pass to Victoria, but
to Ernest Augustus, duke of Cumberland. The latter moved to Germany.
With the expansionism of Bismarck, a choice was given to the king,
George V, to either ally themselves with Prussia or to surrender their
sovereignty. The king left and was eventually exiled in France.
From 1866 to 1945 the then kingdom of Hanover became a province of
Prussia for the next 80 years.
Oldenburg - Pre 1919
This was successively a countship, a duchy and then a grand duchy. From
the twelfth century it was a countship and its greatest extent was
from 1854 onwards. The early reign was by the family of the Saxon duke
Widukind. One of the later rulers, Christian of Oldenburg became King of Denmark, later
of Norway and then of Sweden. He ceded Oldenburg to his brother and
his line of descendants ruled the territory.
Schaumburg-Lippe - Pre 1919
One of the smallest countships with an area of only 342 square kilometers
(132 square miles). It was ruled from 1111 by a series of Counts
until the revolution of 1918.
1919 - 1946
The Free States were part of the German Reich under the Weimar
Constitution of 1919 until 1934 when Hitler passed a law divesting
these States of their independence.
Post 1946 - Independent or Free State
Lower Saxony was only established on 1 November 1946 when the Prussian
province of Hanover was merged with the states of Brunswick, Oldenburg
and Schaumburg-Lippe.
FLAG OF LOWER SAXONY

Graphic from
Flags of the World
Please send any information, comments or suggestions to the addresses as shown on the
HOME PAGE
 |
Date Last Updated: |
26 August 2021 |
| Date First Published: |
26 June 1999 |
Copyright - Firstly, the necessary credit has been given in all
cases where information was obtained. If any person objects to any
material used on these pages they should please contact the author.
Secondly, authority is given to anybody to use the material on these
web pages for non-commercial purposes.








